Diabetes & Breast Cancer
QOL Tree
More Health Problems - Diabetes
Testing & Diagnosis
Pre-Diabetes
Types
Type 2 Risks
Symptoms
Treatment
Management
Hemoglobin A1C
Complications
Sick Day Self Care
Chronic Illness
Emotions
Breast Cancer
Living with Diabetes and dealing with a Cancer Diagnosis, such as for "Breast Cancer"
Diabetes and Breast Cancer
- When breast cancer is serious and life threatening, it is often necessary to remove the breast
- When a woman has this surgery, she can choose to use special padded bras or she can have reconstructive surgery to re-create a breast
- Men who have breast cancer rarely consider reconstruction surgery, but it is an option for them as well
- Body Image and Breasts
- Like diabetes-related complications that cause the surgical removal of a limb, losing one's breast can also be traumatic
- Some women say they feel less of a woman if they have had a mastectomy (surgical removal of the breast)
- These reactions are common and you should know that this is something to talk to your doctor, your family and other cancer survivors about
- The challenge of having diabetes is an extra stress for the man or woman coping with breast cancer
- Having a cancer diagnosis and dealing with the cancer treatment can affect your diabetes control
- Diabetes continues to be a growing problem among American Indians and Alaska Natives
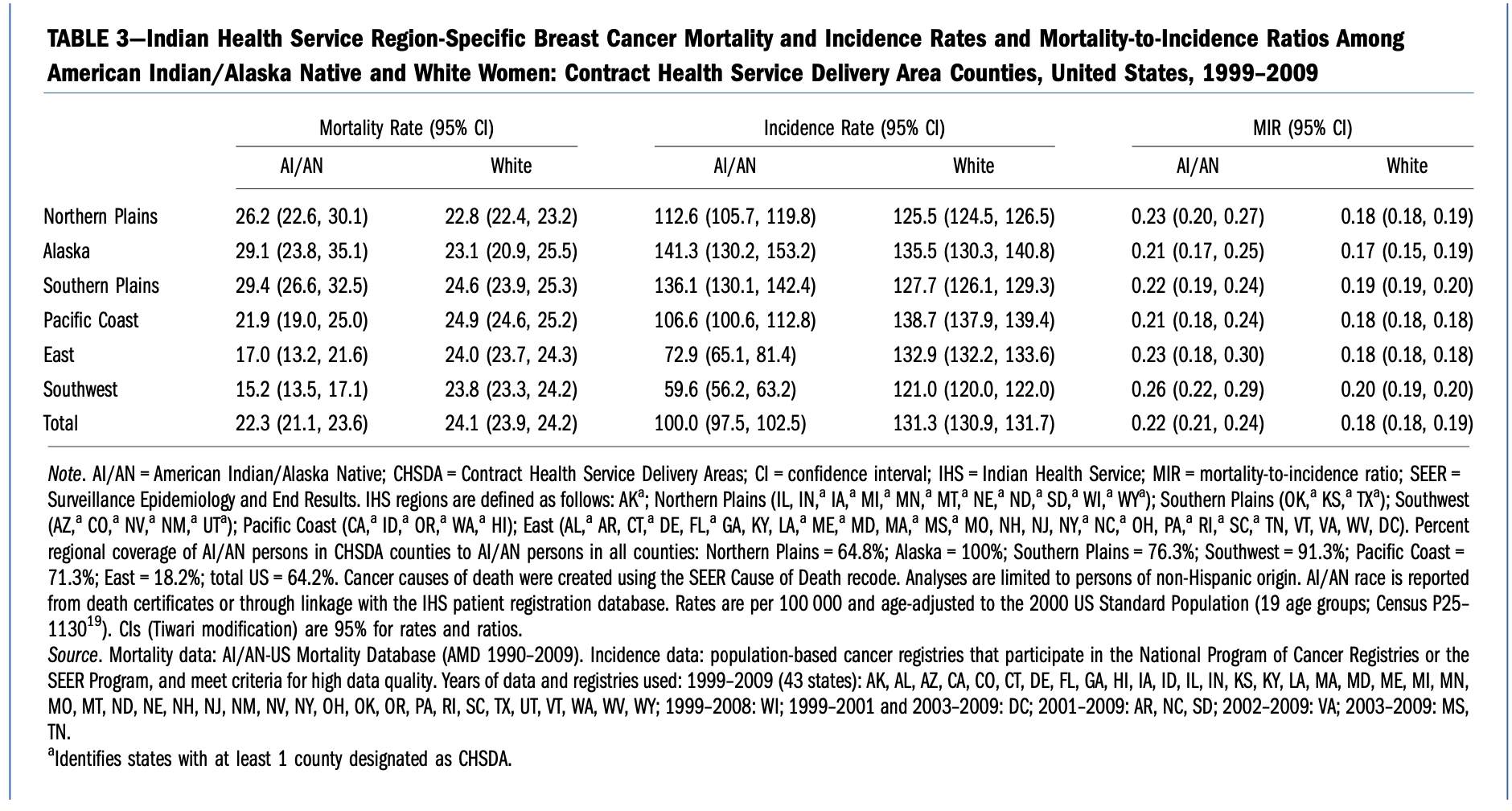
Reference for that table: White A, Richardson LC, Li C, Ekwueme DU, Kaur JS. Breast cancer mortality among American Indian and Alaska Native women, 1990-2009 [published correction appears in Am J Public Health. 2014 Aug;104(8):e6]. Am J Public Health. 2014;104 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S432-S438. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2013.301720
Controlling Your Diabetes During Breast Cancer Treatment
- The goal for people with diabetes is to control the level of blood sugar, including throughout their treatments for cancer
- What is a good blood sugar level?
- Blood sugar level goals:
- Morning fasting = 80 -110
- Before meals = 90 -130
- After meals = < 180 (less than 180)
- Blood sugar level goals:
- Check your blood sugar regularly, as often as your health care provider recommends
- Eat healthy and maintain a normal weight
- Be physically active
Blood Sugar Levels
- It's common to have some difficulty controlling your blood sugars when you also have been diagnosed with breast cancer and are undergoing treatment
- The sugar often will go up, if you are feeling stressed
- It may also go up if you are having physical symptoms from your cancer or treatment, for example, pain
- If you have no appetite and are eating less, your blood sugar can get too low
- This is why it is so important to check your sugars on a regular basis, because your body is going through so many changes - and that can have a great effect on your diabetes
- Whether you are a new diabetic or you've had diabetes for several years, you will want to pay close attention to your blood sugars from the time of your breast cancer diagnosis through the completion of your treatments
Cancer Effects on the Man or Woman who also is diabetic
- The stress of breast cancer diagnosis
- Chemotherapy medicines - side effects vary
- Radiation - side effects vary
- Treatment side effects, for example, infection
- Long term breast cancer treatment side effects, for example, fatigue
Things to do Before Starting Cancer Treatment to help control your blood sugar / diabetes
- Have a check-up with your regular doctor
- Check how your blood sugars are doing before treatment
- Talk about how often you need diabetes checks during treatment
- See your dentist
- Have an exam of your teeth and gums
- Discuss your cancer treatment plan and learn if you need to do any special mouth care
- Ask how often you should see the dentist during treatment
- Ask what symptoms to watch out for
- Get or make a chart to record your home sugar tests
- Keep a chart of your daily blood sugars
- Ask how often you should check your sugars
- Take this record with you to all of your medical appointments
| Blood Sugar Chart | |||||||
 |
Sun | Mon | Tues | Weds | Thurs | Fri | Sat |
| Fasting |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| After breakfast |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| After lunch |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| After supper |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Bedtime |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
- Ask your cancer doctor whether you need any special diet during treatment or on treatment days
- Record your weight at least once a week
- Ask your cancer doctors or health care provider how much you can exercise during treatment, whether chemo, radiation or surgery
- Check your blood sugar level regularly and adjust your medications
Controlling Your Diabetes While Going Through Breast Cancer Treatment
- How Best to Treat Diabetes
- Treatments for diabetes vary, depending on the person and how high their blood sugar is
- Efforts to bring the blood sugar down usually include some or all of the following:
- Diet and exercise
- Oral medication
- Combination of diet, exercise, and pill
- Insulin
For More Difficult-to-Control Diabetes
- If the blood sugar is not responding to pills, insulin may be prescribed
- More than one type of insulin may be recommended
- For some patients (usually young patients), an insulin pump might be prescribed
- Pumps are expensive (several thousand dollars) but some individuals are better able to control their blood sugar with a pump
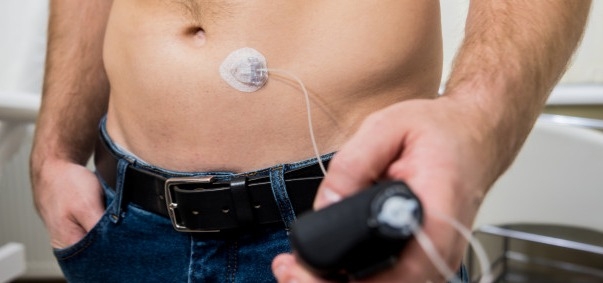
- The pump is worn like a pager at the waist usually
- It has a tiny tube inserted under the skin
- The pump gives a basic dose of insulin throughout the day
- The person with diabetes can increase or decrease the amount of insulin depending on diet and activity
The Glucose Meter
- A glucose meter is a small device used to test for sugar levels
- A drop of blood is placed on a special strip that is inserted into the machine and the machine reads the sugar level
- A doctor will instruct you on
- How often you should test your blood sugar
- How to adjust your medication based on what results you have gotten on the test
What is High or Low Blood Sugar?
- Cancer treatments (surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy) can greatly affect your blood sugar levels
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) is when the test show:
- At or over 240 mg/dl
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) is when the test show:
- Less than 70 mg/dl
Both cancer and diabetes medications have different strengths and have varying lengths of action
- So if you have questions about how your diabetes is being treated, be sure to ask your health care provider
- It usually helps to take your home blood sugar record to the clinic with you
Diabetes Medications
- Uncontrolled high blood sugar over a period of time can cause Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- When the body cannot use the glucose normally, it starts to break down fat and the blood becomes acidic
- Over time high blood sugars cause the complications of diabetes
- These complications can be delayed or prevented by good blood sugar control
- Uncontrolled low blood sugar can cause insulin shock
- From too much insulin or too little food
- Can lead to unconsciousness, coma and even death
- Some have rapid action
- Some are slow acting
- Some are long acting
- Many patients may require a combination of these different medicines
- It is not unusual to try a number of different medicines before finding the right combination and the combination may change as you experience the side effects of cancer treatment
- May help the pancreas make more insulin (the hormone)
- Helps open the cells so the glucose can enter and provide energy for the cell
- Helps the pancreas release more insulin after a meal
- Helps the cells become more sensitive to insulin
- Lowers sugar released by the liver
- Provides needed insulin for the body